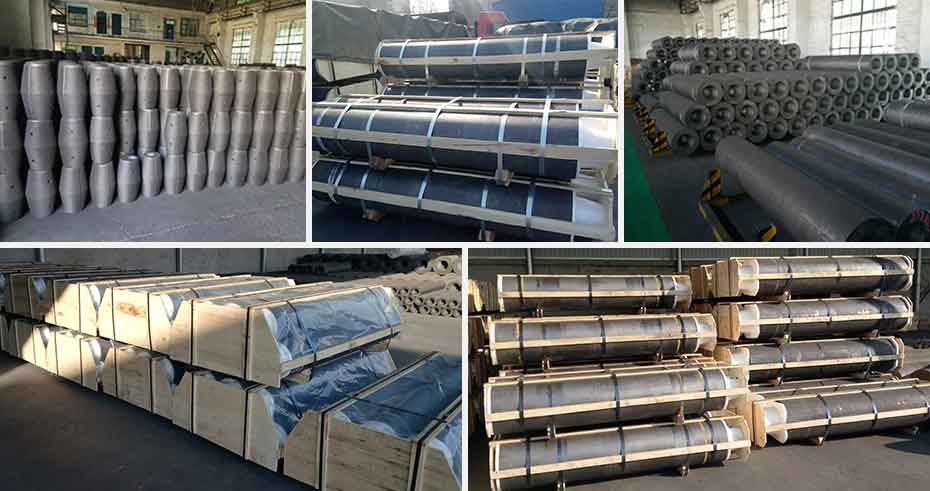
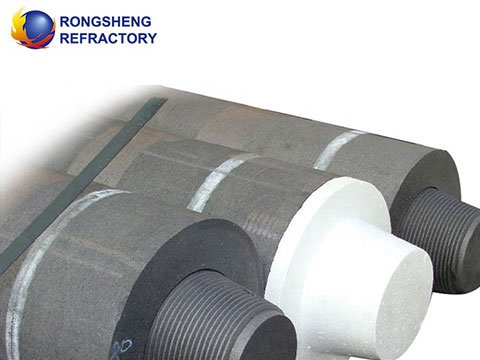
Arc Furnace Electrodes from Rongsheng – Built for Demanding Industries. In steel plants, glass factories, and other high-temperature industries, arc furnace electrodes are the workhorses that keep production running. They conduct massive amounts of electricity into furnaces, creating the heat necessary to melt and refine raw materials.
Choosing the right electrodes isn’t just a technical decision — it’s an investment in operational stability, cost control, and product quality. At Rongsheng, we combine advanced production technology with strict quality control to deliver arc furnace electrodes that perform under pressure and last longer.

What Sets Rongsheng Apart as a Graphite Electrode Manufacturer
As an established graphite electrode manufacturer serving over 120 countries, Rongsheng focuses on three priorities: performance, reliability, and customization.
-
- Performance – Our electrodes are engineered to carry high currents without significant loss, providing efficient energy transfer and faster melting cycles.
- Reliability – Built from high-quality needle coke and binder pitch, they resist oxidation, cracking, and premature breakage.
- Customization – We can produce a wide range of diameters, lengths, and connection types to suit different furnace sizes and operational requirements.
Whether your plant needs electrodes for standard power, high power, or ultra-high power furnaces, we deliver solutions tailored to your process.
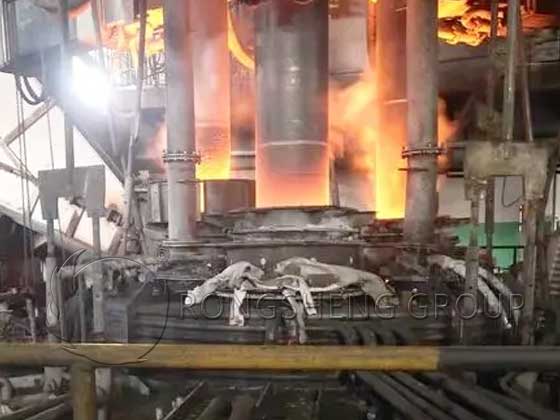
The Role of Arc Furnace Electrodes in Industry
Arc furnace electrodes are primarily used in electric arc furnaces (EAF), where electricity is converted into heat via an arc discharge between the electrode tip and the furnace charge. In an EAF, temperatures can exceed 3000°C, allowing for the rapid melting of scrap steel, alloys, and other raw materials.
But their role doesn’t stop at steelmaking — they also power furnaces in specialty alloy production, non-ferrous smelting, and chemical manufacturing.

Rongsheng’s Graphite Electrode Applications
Our arc furnace electrodes are designed for multiple high-temperature applications, with steelmaking as the core focus.
1. Metallurgical Industry
Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking
The largest single use of arc furnace electrodes, accounting for 70%–80% of global consumption. The electrode tip discharges a high-temperature arc exceeding 3000°C, melting scrap steel and enabling refining processes such as desulfurization and dephosphorization.
In 2024, ultra-high-power electrodes showed a 20%–40% reduction in resistivity, improving energy efficiency.
Oil-Fired Electric Furnace Smelting
Used in producing industrial silicon, yellow phosphorus, and ferrosilicon, where both arc heat and resistance heat are applied.
With antioxidant-treated electrodes, silicon consumption per ton drops from 150 kg to 100 kg (2024 data).
2. Chemical and Materials Manufacturing
High-Purity Material Production
For abrasives such as corundum and silicon carbide, our electrodes deliver heat at over 2000°C to achieve the desired crystal structure and purity.
Aluminum Electrolysis Anode
While structurally different from standard arc furnace electrodes, the material properties are closely related. These components enable the electrolytic reduction of aluminum oxide to metallic aluminum.
3. Specialty Industries and Processing
Resistance Furnace Heating Elements
Used in graphitization furnaces, our electrodes maintain a volume density of 1.72 g/cm³ even after 240 hours at 1200°C.
Special-Shaped Product Processing
Electrode blanks can be machined into crucibles, hot-die-casting molds, and other high-temperature products. Producing quartz glass requires about 10 tons of electrode blanks per ton of electric melting tube.
Manufacturing Excellence from Raw Material to Finished Electrode
Our production process is built for precision.
-
- Raw Material Selection – Only premium needle coke and binder pitch are used.
- Crushing, Screening & Dosing – Particle size distribution is carefully controlled.
- Kneading & Forming – Uniform mixing ensures structural integrity.
- Baking & Impregnation – Increases density and mechanical strength.
- Graphitization – Transforms carbon into high-conductivity graphite at temperatures up to 3000°C.
- Machining – CNC equipment ensures perfect dimensions and tight nipple fit.
- Inspection – Each electrode undergoes resistivity, density, and mechanical strength testing.
The result: over 98% qualification rate and electrodes that consistently perform in heavy-duty operations.
Why Steel Plants Choose Rongsheng Arc Furnace Electrodes
-
- Lower Operating Costs – Longer service life means fewer replacements, less downtime, and reduced labor costs.
- Energy Efficiency – Low resistivity ensures more heat is generated in the melt, not wasted in the electrode.
- High Repurchase Rate – Many of our clients are repeat customers, trusting our consistency year after year.
- Global Track Record – Our electrodes are in use from Asia to Europe to South America.
Customer Success Story
A Southeast Asian steel producer operating multiple 100-ton EAFs replaced their previous supplier with Rongsheng UHP arc furnace electrodes.
After six months, they reported:
-
- Electrode life extended by 18%
- Reduction in breakage incidents
- Lower overall cost per ton of steel
This not only improved furnace productivity but also reduced unplanned maintenance shutdowns.
The Right Electrode for Your Process
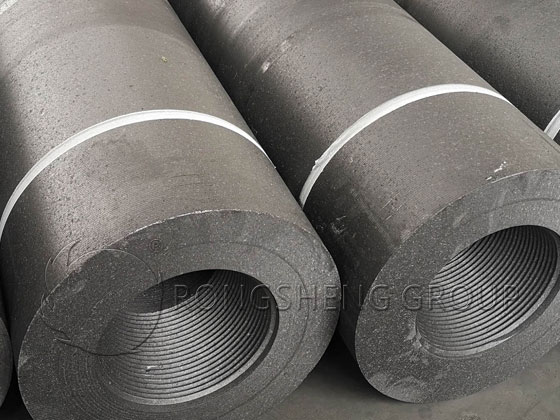
Whether your operation requires RP, HP, or UHP electrodes, Rongsheng can supply the grade and size that best fits your furnace and melting profile. We offer diameters from 100 mm to 700 mm and lengths up to 2700 mm, with all industry-standard nipple types available.
Conclusion & Call to Action
Arc furnace electrodes are the backbone of modern steelmaking and many other high-temperature industrial processes. As a dedicated graphite electrode manufacturer, Rongsheng delivers products that combine quality materials, precise manufacturing, and proven field performance.
If your plant needs reliable, long-lasting, and efficient arc furnace electrodes, Rongsheng is ready to supply — backed by years of experience and a global client base.
📩 Contact us today for a free consultation and quote.
🌐 Visit our website to explore our complete electrode product range.